ZTNA vs. ZTAA vs. ZTA: Which One Should You Choose?


Zero Trust security provides your employees, partners and contractors with secure remote access to your network. By managing access through identities and devices and not through networks and transitive trust, actors are constantly validated and bad actors are denied access to your crown jewels.
Zero Trust architecture has a number of different security models: ZTNA, ZTAA and ZTA. It’s important to understand the differences between them, because they will determine the level of protection of your network as well as your security posture. This blog post will explain each one and help you understand which solution is best suited to answer your zero cybersecurity needs.
ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access) is the most widely used implementation of the Zero Trust model and what most people think of when they hear “Zero Trust”. Also dubbed “software-defined perimeter (SDP)”, ZTNA architecture grants users access to assets and systems in the network only after they have been verified and authenticated.
ZTNA is based on micro-segmentation and isolation of networks. It is a VPN replacement, enabling secure access of users from different locations and devices without being dependent on corporate networks. In this era of remote work, ZTNA is a good solution for CISOs and IT managers who need to find a quick an simple solution for their employees
A common ZTNA model will look like this. As you can see, the cloud broker sends all users and devices, no matter if they originated from the external or internal network, to get authenticated before providing access.
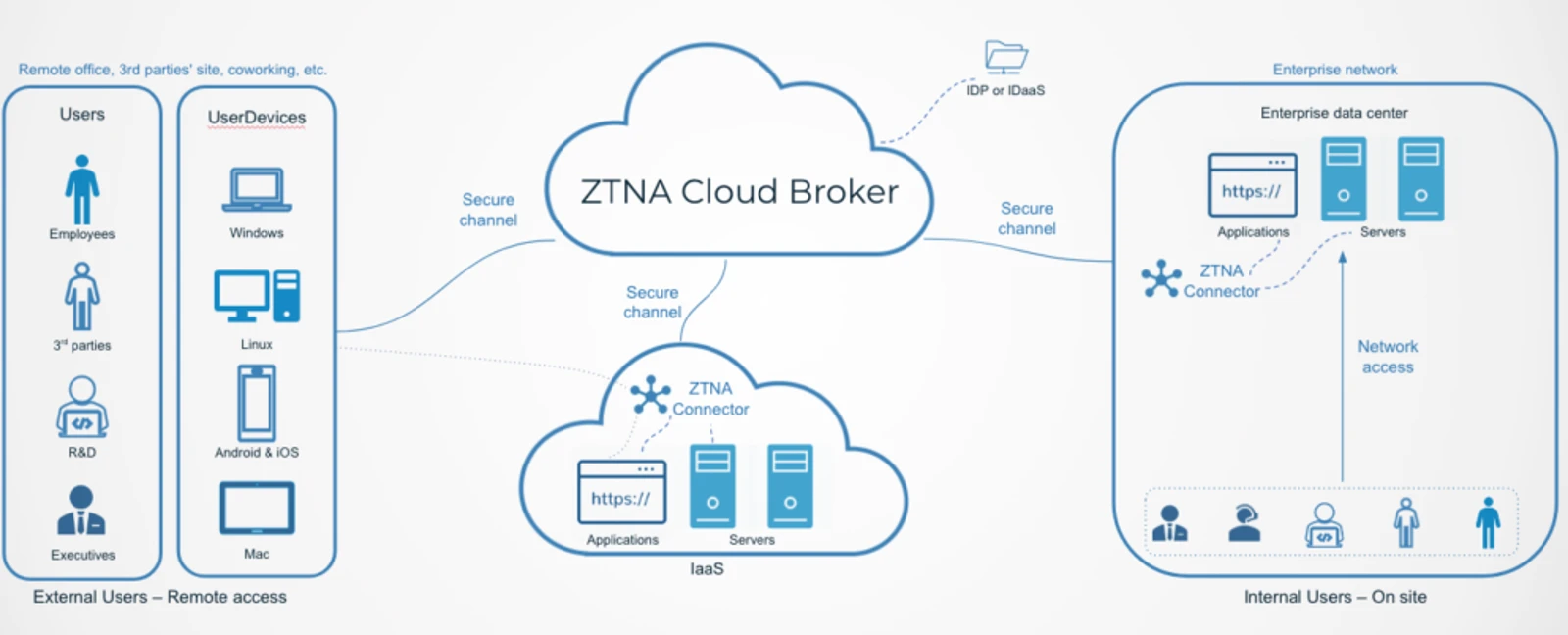
Blocks hackers that could previously access systems and inject malware once they entered the perimeter.
Replaces VPNs, especially during the remote work era
Provides secures access from external networks
Does not protect apps
Requires trusting the ZTNA provider
Does not secure access from offline and closed networks like OT, SAP and ERP
While ZTNA protects the network, applications are left vulnerable. This is where ZTAA comes on. ZTAA operates according to the same Zero Trust principles like ZTNA. However, it assumes all networks are compromised and opens up access to applications only after users and devices are authenticated.
Blocks hackers that enter the network
Protects apps
Requires trusting the ZTAA provider
Does not secure access from offline and closed networks like OT, SAP and ERP
Zero Trust Access (ZTA) is a method that provides end-to-end zero trust, across all networks, apps, systems data centers and the rest of the architecture components. Based solely on identity-based access, true Zero Trust is not bound to specific networks or platforms. Therefore, it provides complete zero trust across the entire organizational architecture, even for unique and offline networks like the industrial floor or ERP.
ZTA encompasses ZTNA and ZTA, but provides a pure Zero Trust approach. Not only is it completely identity based, it also applies the approach to the provider itself. A ZTA provider does not require the user to trust it all.
While ZTNA and ZTAA providers access the organization’s data so they can validate access to it, a true zero trust provider does not have any visibility into the organization. This is especially valuable for organizations that value their data privacy.
A ZTA model will look like this:
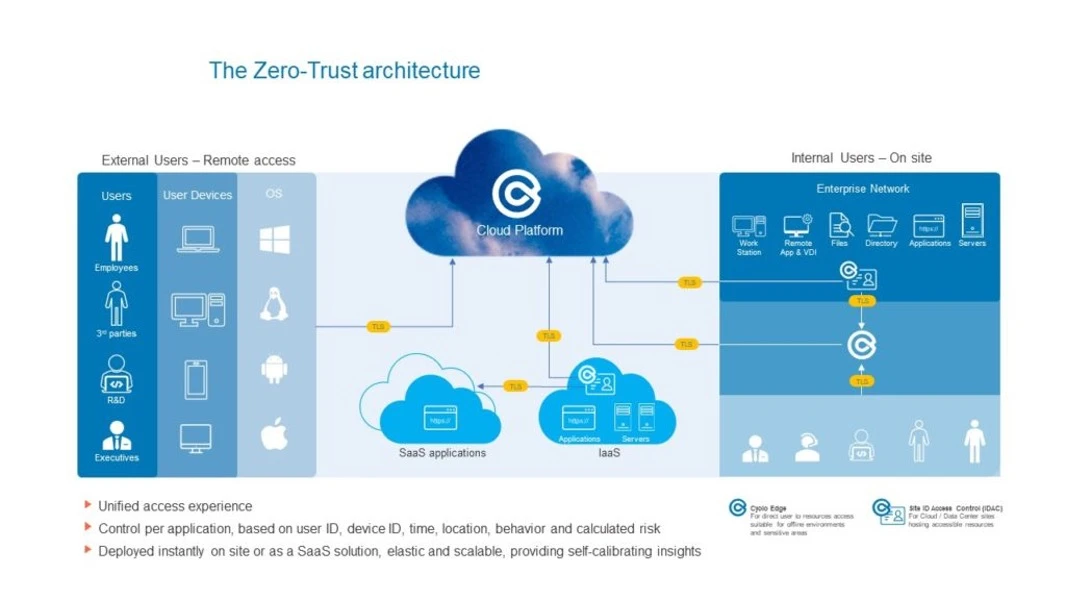
As you can see, no inbound network traffic is allowed. All the customer data and secrets are kept in the component that resides in the organizational secure environment and are not accessible even to the ZT provider. This includes the policies and password vault that are also signed by the customers keys (certificates) and are not visible to anyone.
Blocks hackers that try to access any part of the network architecture
Covers all networks and protocols
The ZT provides does not have access to the customer data - no data leaves the network
Requires changing the organizational approach from the perimeter security model
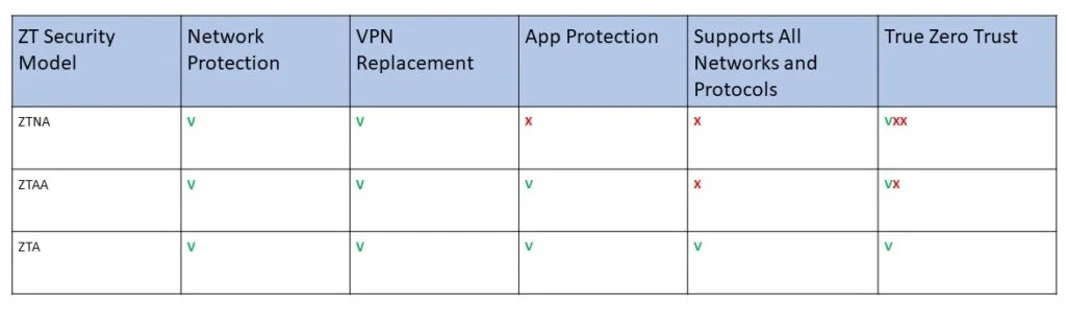
The shift in organization network architecture requires quick adoption of new security methods. Zero Trust is a convenient VPN replacement, adjusted to today’s world where users are connecting across the globe from multiple devices. When choosing a Zero Trust solution, CISOs, CIOs and IT Managers can decide to secure the network (ZTNA), applications (ZTAA) or their complete architecture (ZTA).

